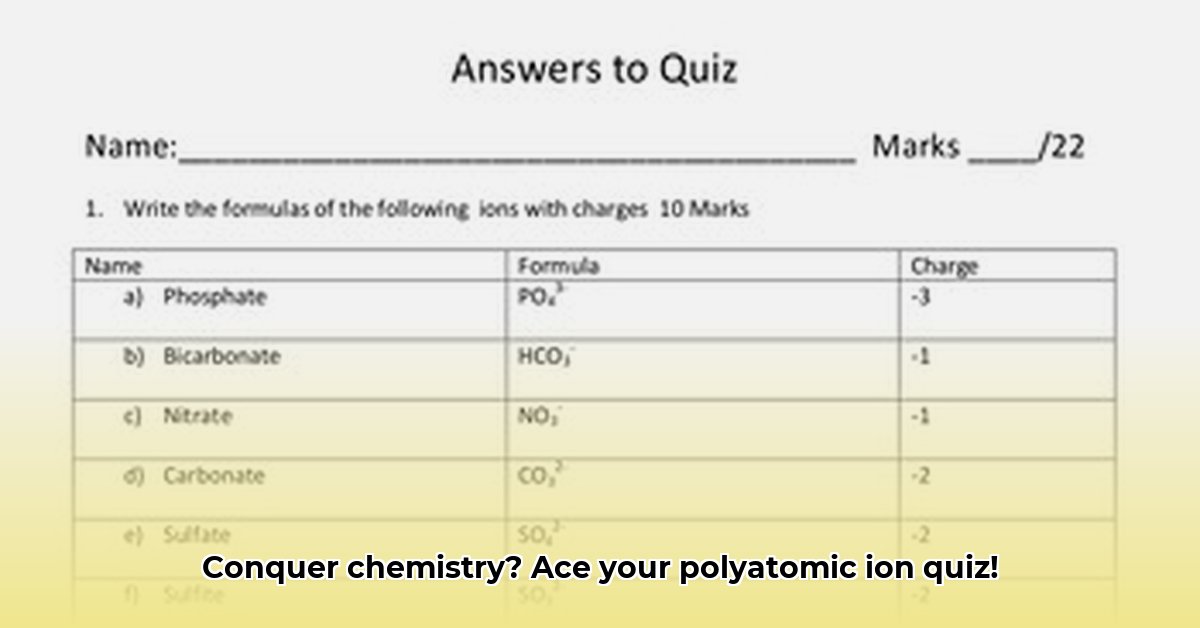
Conquering chemistry often hinges on understanding polyatomic ions—groups of atoms acting as single, charged units. This guide helps you master polyatomic ions and ace your exams, moving beyond rote memorization to build lasting comprehension. Test your knowledge with this polyatomic ions quiz.
Understanding Polyatomic Ions: The Fundamentals
Polyatomic ions are fundamental building blocks in chemistry, appearing in various compounds and reactions. Understanding their behavior unlocks a deeper understanding of many chemical processes. They are crucial for predicting and describing chemical interactions. Why is mastering them so important? Because they're the key to understanding many complex compounds and their interactions.
Demystifying Polyatomic Ions: Charge and Structure
A polyatomic ion (a group of covalently bonded atoms with an overall charge) is a collection of atoms that behave as a single charged unit. Understanding their structure and charge is key. This involves understanding oxidation states (the apparent charge of an atom in a molecule) and how those states combine to give the overall charge of the ion. The naming conventions also play a crucial role. For example, knowing the rules for naming anions (negatively charged ions) helps you quickly identify an ion like sulfate (SO₄²⁻).
Effective Learning Strategies: Beyond Rote Memorization
Simply memorizing polyatomic ion names and formulas isn't effective. A more successful approach involves employing various learning strategies which reinforce understanding and lead to long-term retention.
Flashcards: Create flashcards with the ion name on one side and the formula on the other. Regularly quiz yourself.
Mnemonics: Use acronyms, rhymes, or memorable phrases to connect ion names and formulas—improving recall.
Spaced Repetition: Review material at increasing intervals, a scientifically proven technique to boost long-term retention.
Interactive Quizzes: Use online games and quizzes to test your knowledge actively. Immediate feedback pinpoints areas needing more focus.
Did you know? Studies show spaced repetition improves retention by up to 90% compared to massed practice. (Source: Cepeda et al., 2006, Psychological Science)
But remember: linking names and formulas to the ions' chemical structures is crucial for true understanding, not just superficial memorization. Visualizing the atoms’ arrangement and bonds clarifies how these ions behave.
Interactive Resources: Elevate Your Learning
Many online resources can make learning polyatomic ions engaging. However, their effectiveness varies.
| Resource Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Online Quizzes (Sporcle, etc.) | Fun, rapid feedback, good for basic knowledge assessment | Often superficial; mainly useful for memorization, not deep understanding |
| Educational Websites | Offer comprehensive explanations, diagrams, and practice problems. | Can be overwhelming; might require self-discipline to navigate effectively. |
| Educational Videos | Offer visual learning; experts explain complex concepts clearly. | Less interactive; demands focused attention. |
Choose resources that best suit your learning style. Experiment to discover your preferred method. Remember, engagement is key to effective learning.
Practice Problems: Test Your Knowledge
Let's test your understanding with gradually increasing difficulty. The goal is not just correct answers, but understanding the underlying principles.
Beginner:
What is the formula for the hydroxide ion? (Answer: OH⁻)
What is the name of CO₃²⁻? (Answer: Carbonate)
Name this ion: ClO⁻ (Answer: Hypochlorite)
Intermediate:
What charge does the phosphate ion (PO₄) carry? (Answer: 3-)
What is the formula for the ammonium ion? (Answer: NH₄⁺)
Name this ion: MnO₄⁻ (Answer: Permanganate)
Advanced:
- Predict the charge of the chromate ion (CrO₄). (Answer: 2-) Hint: Consider chromium's common oxidation states.
Diving Deeper: Advanced Concepts
Understanding electron configuration and oxidation states reveals the fundamental principles behind polyatomic ion formation. This allows you to predict the formulas and charges of various ions instead of relying solely on memorization.
The Future of Polyatomic Ion Learning
Chemistry education’s evolution includes personalized learning platforms driven by artificial intelligence. These platforms will adapt to individual needs, providing targeted practice and feedback. Augmented and virtual reality hold immense potential for visualizing molecular structures, transforming abstract concepts into immersive learning experiences. These innovations aim to make chemistry education more engaging and effective.
Pivotal Points:
- Beyond Rote Memorization: Effective learning involves strategic techniques like flashcards, mnemonics, and spaced repetition, alongside a focus on understanding the chemical structure.
- Interactive Learning: Online quizzes and educational websites offer valuable supplementary tools, but their effectiveness depends on individual learning styles and preferences.
- Structural Understanding: Connecting names and formulas with the actual three-dimensional structure of ions is key to comprehension. This allows you to predict properties of unknown ions.